Overview
Over pronation of the foot is commonly referred to as “flat feet.” Many middle-aged men and women suffer from over pronation over time and as a result of wearing poor-fitting shoes, continuing with repetitive exercising habits, or walking in high heels for long periods over several years. Regular speed-walkers often experience over pronation as well as a result of this activity.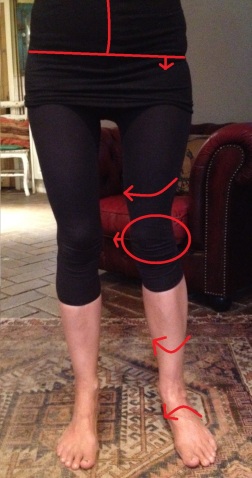
Causes
Over-pronation occurs when the foot collapses too far inward stressing the plantar fascia (the area underneath the arch of the foot.) Normally, one pronates every time he or she walks, but excessive pronation is called over-pronation. When this occurs it can cause pain in the feet, knees, hips, low back and even the shoulder. Decreasing over-pronation, which is very prominent in runners, will help add endurance, speed and efficiency to your run and ultimately place less stress on your body.
Symptoms
Over-Pronation may cause pain in the heel of the foot, the foot arch, under the ball of the foot, in the ankle, knee, hip or back. The symptoms may be localized to one particular area of the foot or may be experienced in any number of combinations. Standing for long periods of time, walking and running may become difficult due to the additional stress and/or discomfort accompanied with these activities. Upon Visual Inspection, when standing the heels of the foot lean inward and one or both of the knee caps may turn inward.
Diagnosis
Bunions, calluses and crooked toes may indicate alignment problems. So, it is important to ascertain the condition of a client’s toes. Check the big toe to determine if the first joint of the toe is swollen, has a callus or bunion, and/or looks as though it abducts (i.e., hallux valgus) rather than pointing straight ahead. Also, look to see if the lesser toes seem to “curl up” (i.e., the person has hammer or claw toes). This may be indicative of damage to, or inflexibility of the plantar fascia caused by excessive flattening of the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
When you see the doctor, he or she will likely perform a complete examination of your feet and watch you walk. The doctor will need to take x-rays to determine the cause of your flat feet. In some cases, further imaging may be needed, especially if your symptoms are severe and sudden in nature. Once you are properly diagnosed, your doctor will create an appropriate treatment plan. There are several options to correct overpronation, such as orthotics. In many cases, overpronation can be treated with non-surgical methods and over-the-counter orthotics. In severe cases, however, custom-made orthotics may work better. Orthotics provide arch support and therefore prevent collapse of the arch with weight bearing. They are made of materials such as spongy rubber or hard plastic. Your doctor will also want to examine your footwear to ensure they fit properly and offer enough medial support. Extra support and stability can be achieved with footwear that has a firm heel counter. If you are experiencing pain, you should be able to use over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen to relieve symptoms.
Prevention
Pronation forces us to bear most of our weight on the inner border of our feet. Custom-made orthotics gently redistributes the weight so that the entire foot bears its normal share of weight with each step we take. The foot will not twist out at the ankle, but will strike the ground normally when the orthotics is used. This action of the custom-made orthotics will help to prevent shin splints, ankle sprains, knee and hip pain, lower back pain, nerve entrapments, tendonitis, muscle aches, bunions, generalized fatigue, hammer toes, and calluses.